The main purpose of compacting is converting loose powder into a green compact of accurate shape and size. The techniques adopted for compacting are pressing, centrifugal compacting, extrusion, gravity sintering, and rolling.
Pressing: The metal powders are placed in a die cavity and compressed to form a component shaped to the contour of the die (Figure 21.29). Mechanical presses are used for compacting objects at low pressure. Hydraulic presses are for compacting objects at high pressure.
Centrifugal Compacting: In this method, the mould after it is filled with powder is rotated at high speed to get a compact of high and uniform density at a pressure of 3 MPa due to centrifugal force. This method is normally employed for heavy metals such as tungsten carbide.
Extrusion: This method is employed to produce the components with high density. Both cold and hot extrusion processes can be used. In cold extrusion, the metal powder is mixed with binder and then this mixture is compressed into billet. The binder is removed before or during sintering. The billet is charged into a container and then forced through the die by means of ram. Cold extrusion process is used for cemented carbide tools.
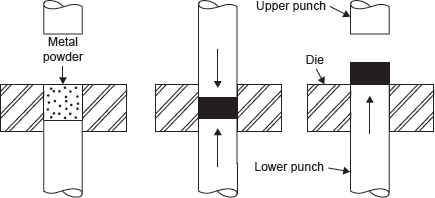
Figure 21.29 Compacting (Pressing)
In the hot extrusion, the powder is compacted into billet and is heated to extruding temperature in non-oxidizing atmosphere. The billet is placed in the container and extruded through a die. This method is used for refractive barium and nuclear solid materials.
Gravity Sintering: This process is used for making sheets for controlled porosity. In this process, the powder is poured on ceramic tray to form a uniform layer and is then sintered up to 48 h in ammonia gas at high temperature. The sheets are then rolled to desired thickness. Porous sheets of stainless steel are made by this process and popularly used for fitters.
Rolling: This method is used for making strips and rods having controlled porosity with uniform mechanical properties. In this method, the metal powder is fed between two rolls which compress and interlock the powder particles to form a sheet of sufficient strength. The metals that can be rolled are copper, brass, bronze, nickel, stainless steel, and monel.
Leave a Reply