The mechanism of material removal in USM is brittle fracture of the layer work material. A tool of ductile and tough material is used for vibration with high frequency; and a continuous flow of abrasive slurry is used between the vibrating tool and work surface. The impact of vibrating tool on abrasive slurry fractures the hard and brittle layer of work surface. The tool material of ductile and tough materials wears out at low rate. Generally, soft steel is used for tool materials.
The main components of USM machine are (a) transducer and acoustic head with tool, (b) feed mechanism, and (c) the abrasive slurry and pumping machine. High frequency AC current is supplied to the transducer, which converts it into mechanical vibration. Due to temperature generation in transducer, cooling fluid is used which is shown in Figure 23.3. The vibration is supplied to acoustic head, which amplifies the vibration and transmits tool. Slurry is supplied between the tool and work through slurry pump. During material removal process, tool is fed into the work by counter weight, (a) Ultrasonic machining setup (b) Ultrasonic machining setup spring, and pneumatic/hydraulic or motor mechanism. The tool diameter should not be larger than 1.5–2 times the diameter of the end of the concentrator.
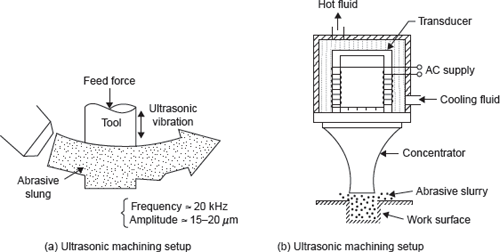
Figure 23.3 A Conceptual Diagram for USM
The most common abrasives used are boron carbide (B4C), silicon carbide (Sic), corundum (Al2O3), diamond, and boron-sili-carbide. Water is the most commonly used fluid in the slurry; other liquids such as benzene, glycerol, and oils are also used. The material removal rate decreases with increase in viscosity of the fluid.
Leave a Reply